BY LETTER
Rigel
Galactography > Sephirotic Empires > Metasoft Version Tree
Galactography > Systems and Worlds > Systems & Worlds Q - R
Galactography > Systems and Worlds > Systems & Worlds Q - R
Beta Orionis - a brilliant star in Orion | |
 Image from Steve Bowers | |
| Rigel A has a very strong stellar wind, and exhibits powerful flares and prominences which provided material for initial starlifting efforts. Inset; the G-type star Sol for scale. | |
Rigel - Data Panel | |
| System Name | Rigel, Beta Orionis |
|---|---|
| Stellar Components | 4 1) Rigel (Beta Orionis A) 2) (Beta Orionis Ba) 3) (Beta Orionis Bb) 4) (Beta Orionis C) |
| Location | - Distance from Sol: 863 ly (J2000) - Constellation: Orion |
 Image from Trolligi | |
| As seen from Rigel Ba,Bb and C, the primary star (A) is very bright, despite its distance of more than 2500AU. From here Rigel A shines with 2 percent of the Sun's brightness as seen from Earth, or 8200 times as bright as a full Moon. | |
Primary - Rigel A | |
| Names | Rigel, Beta Orionis A, 19 Orionis A, HD 34085 A, HIP 24436 A, HR 1713 A |
|---|---|
| Physical characteristics | - Mass: 21 x Sol - Radius: 77.44 x Sol - Oblateness: 0.026 - Temperature: 12,100 Kelvin - Luminosity: 115,300 x Sol (bolometric) - Spectral type: B8 Iae - Rotation period: 156.7 days - Age: 8 million years |
| Colonisation date | 3808 AT Joint mission Metasoft and Taurus Nexus |
| System | A number of hot brown dwarfs orbit Rigel A. 1) Sepeptu: L1 brown dwarf (T=2211 K) Semi-major axis = 56.29 AU, Orbital period = 92.11 years, Eccentricity = 0.068, Mass = 17.05 x Jupiter, Radius = 2.07 x Jupiter 2) Le Nxo: L6 sub-brown dwarf (T=1824 K) Semi-major axis = 117.08 AU, Orbital period = 276.35 years, Eccentricity = 0.094, Mass = 11.8 x Jupiter, Radius = 1.6 x Jupiter 3) Tarden: M8 brown dwarf (T=2580 K) Semi-major axis = 398.6 AU, Orbital period = 1,735.3 years, Eccentricity = 0.041, Mass = 28.95 x Jupiter, Radius = 2.88 x Jupiter |
Orbit of B and C stars around Rigel A | |
| Orbital characteristics | - Average separation: 2,513.5 AU - Orbital period: 23,984.4 years |
|---|---|
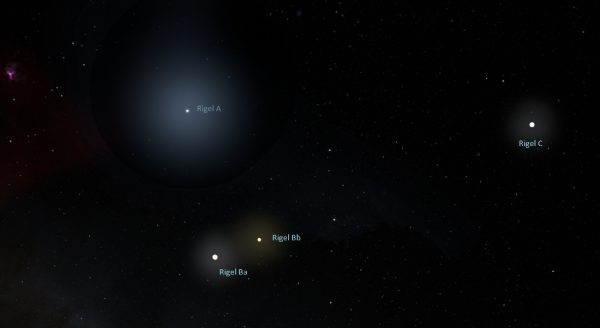 Image from Steve Bowers | |
| Rigel A, Rigel Ba/Bb, and Rigel C | |
Rigel B (double star: Ba and Bb) | |
| Ba | Names: Beta Orionis Ba, 19 Orionis Ba, HD 34085 Ba, HIP 24436 Ba, HR 1713 Ba |
|---|---|
| Physical characteristics | - Mass: 2.94 x Sol - Radius: 1.98 x Sol - Oblateness: 0.083 - Temperature: 12,358 Kelvin - Luminosity: 81.63 x Sol (bolometric) - Spectral type: B9V - Rotation period: 0.59 days - Age: 8 million years |
| Bb | Names: Beta Orionis Bb, 19 Orionis Bb, HD 34085 Bb, HIP 24436 Bb, HR 1713 Bb |
| Physical characteristics . | - Mass: 2.11 x Sol - Radius: 1.68 x Sol - Oblateness: 0.05 - Temperature: 9,649 Kelvin - Luminosity: 21.98 x Sol (bolometric) - Spectral type: B9V - Rotation period: 0.647 days - Age: 8 million years |
| Ba Bb binary orbit | Orbital characteristics: - Average separation: 0.1544 AU - Orbital period: 9.86 days - Eccentricity: 0.1 |
Rigel C | |
| Names | Beta Orionis C, 19 Orionis C, HD 34085 C, HIP 24436 C, HR 1713 C |
|---|---|
| Physical characteristics | - Mass: 2.94 x Sol - Radius: 1.98 x Sol - Oblateness: 0.083 - Temperature: 12,358 Kelvin - Luminosity: 81.63 x Sol (bolometric) - Spectral type: B9V - Rotation period: 0.59 days - Age: 8 million years |
| B C binary orbit | Orbital characteristics: - Average separation: 31.74 AU - Orbital period: 63.2576 years |
| Planet orbiting around B and C | 1) Vwreeftt: L3 sub-brown dwarf (T=1921 K) Semi-major axis = 156.6 AU, Orbital period = 692.3 years, Eccentricity = 0.054, Mass = 12.81 x Jupiter, Radius = 1.65 x Jupiter |
System
Rigel is a quadruple star system consisting of a very luminous B-type blue supergiant, as well as 3 smaller stars in a distant orbit, about 860 light years from Solsys in the constellation of Orion. Rigel owes its huge fame from how bright it is, appearing as a +0.13 magnitude star and the seventh brightest star in the skies of Solsys' planets.Barely 8 million years old, Rigel A started its life as an O-type star slightly more massive than it currently is. Because high-mass stars lose mass so easily, Rigel A has always been considered a very good candidate for starlifting, which has resulted in one of the most efficient starlifting rigs in the Terragen sphere. Rigel A is orbited by 3 young, hot bodies: Sepeptu, a brown dwarf, Le Nxo, a planet (not quite large enough to exhibit deuterium fusion, but very hot due to the proximity of Rigel A), and Tarden, another brown dwarf. These objects each have extensive moon systems.
Rigel B-C is the smaller triple system orbiting Rigel, every 24 thousand years. It consists of 3 B-type dwarfs, two (Ba and Bb) orbiting each other in just under 10 days and the third orbiting the pair every 63 years. Orbiting the trinary every 700 years or so is another young planet, known as Vwreeftt, which is somewhat more massive than Le Nxo.
The Rigel star system has a large and ragged Oort cloud, consisting of many objects thrown out of the system during its formation. Some of the objects are planemo-sized, as big as Mars (or larger), and despite their distance they are illuminated by the rays of Rigel A to various degrees so are not completely dark.
 Image from Trolligi | |
| Vwreeftt, before the construction of its suprashell. This world follows a wide orbit around both the double star Rigel B and Rigel C; only six million years old, the planet is still radiating the heat of its formation. | |
History
An early mission to Rigel set off in 1709, launched by K4H on behalf of the Federation of Sophonts, but this very-long-duration mission would not arrive until 4231 AT. A much faster fleet of exploration ships was launched in 2299, a joint venture by Metasoft and the Taurus Nexus. This joint fleet arrived in 3808, by which time the Taurus Nexus no longer existed. However the news of the dissolution of the Taurus Nexus did not reach Rigel until fifty years later, transmitted by comm-laser from the outermost extent of the then-current wormhole nexus.Metasoft was therefore the major partner in the development of the Rigel star system, and the vecs and their transapients began to develop a network of infrastructure around the brilliant Rigel A star. Although the objects orbiting Rigel A represented a rich source of construction material, they were also bathed in strong UV light, so a number of specialised vecs and aioids were developed which could thrive in this environment. Large power collection swarms were built to collect and re-direct the energy of this blue-white star for a variety of purposes.
Meanwhile the biont modosophonts who made up the ex-Taurus Nexus contingent began to develop their own megastructures around Vwreeftt. Using the extensive system of moons, the Vwreeftt bionts began to construct a Clarke ring of unconnected habitats, which were eventually joined up into a continuous orbital ring structure. Eventually this structure was expanded into a full-scale supramundane shell. The ex-Taurus Nexus faction remained independent, but formed increasingly close links with Metasoft and with the Terragan Federation, which had absorbed many of the old Taurus colonies by this time.
A number of Backgrounder factions started arriving in the 3950s, followed by several ships sent by the Silicon Generation from the (then) fringes of the Terragen Sphere. These factons soon fell into conflict, especially over the prized territories of the deep space planemos in the Oort Cloud. When the Metasoft Version Tree tried to intervene, the local Silicon Generation faction (known as the Emotive Cognation) started to attack Metasoft construction sites in the Rigel star system and elsewhere from 4044 onwards. This conflict (known as the First Vec War) dragged on for a century, and ended in defeat for the Cognation.
Shortly after the end of the First Vec War, the first wormhole arrived in the Rigel system. Over the next century Metasoft began to upgrade the infrastructure in the inner system rapidly, culminating in the creation of a Void Factory and a Weylforge intended to construct void motes and wormholes, a project which would allow Rigel to become an important Node system in the Wormhole Nexus.
The Oort Cloud became mostly a Backgrounder playground, although some deep space objects were taken over by the K4H modosophonts when they finally arrived in 4231. Another faction that began to arrive during this period was made up of refugees from the Conver Wars. After the First Vec War many of the Backgrounder factions in the Oort Cloud started to build amicable links with the Metasoft controllers of the inner system, and began to receive power and advanced technology from them in exchange for deep space secure storage. However a significant number of Backgrounders declined to participate in the greater Rigel culture, and became even more isolationist.
During the Version War the wormhole trunk route was shrunk down to a non-traversable radius, allowing information to be transmitted but not spacecraft. The closest Dominion world was a hundred light years away, and a few warships from that empire approached the edge of the Rigel Oort cloud, but the newly emerged archai in the inner system were alerted by a causality fortress network of comm-gauge wormholes in the cloud, and the Dominion warships were targeted by beam weapons before they could cause any significant damage.
When the Orion Federation emerged in the post CompEmp era the Rigel system did not become part of it but remained loyal to Metasoft. However the Orions maintain a large embassy habitat and computation cluster in this system.
Rigel in the Current Era
The inner two objects orbiting Rigel A (Sepeptu and Le Nxo) have been extensively mined for resources to build Rigel A's starlifting rig, as well as its surrounding Dyson swarm and Class 2 sun-lines. Power collected from Rigel A maintains the thirty wormholes that are distributed widely around the star, and is also beamed towards a large number of very distant objects and habitats in the Oort Cloud, supporting a population of hundreds of trillions of Backgrounders and other groups.These worlds also have extensive moon systems, which have been retained to house a population of adapted vecs and other clades. The third "planet" (a brown dwarf), Tarden, as it is located in Rigel A's habitable zone, also has a large supraplanetary shell suspended above it, with a variety of different environments enclosed beneath a sunshield designed to filter out the strong ultraviolet light of the primary star.
Further out from these three worlds are a number of Banks Orbitals surrounding the star at many different angles, housing several trillion modosophonts of all kinds. The most populous orbital is known as Somewhere, a word borrowed from an ancient Earth language.
The innermost ten wormholes are co-orbital with the B/C stellar trio, and the others lie outside of this. The wormhole trunk route that passes though this system leads straight to the Orion Federation empire and the Orion OB1c association.
Vwreeftt now has a thin supraplanetary shell suspended above it; this world is largely inhabited by bionts ovf various types, although the ancient boundaries between different types of sophont life have become increasingly blurred in recent millenia.
A number of ringworlds surround the C component, which is a more favourable place for these as the B component is a binary and can destabilise such rings due to their varying gravitational forces. It is a common sight to see augmented Sailors of the Ebon Sea racing around this system, which is a popular sporting attraction that occurs at regular intervals.
Nearby Stars
The nearby star β 555D is not a true member of this stellar group. This star, a K-type dwarf, is just under half a light year from Rigel A, but is not gravitationally bound to the group and is several billion years older. This star was colonised by Panvirtual Solipsists in 7131 AT, and for thousands of standard years there was no significant interaction between the Solipisists and the Sephirotic inhabitants of Rigel.Since the start of the Current Era the Panvirts have opened up a number of communication channels, and sometimes send virtual entities as visitors, tourists or observers to Rigel's complex cybercosms. Sometimes this movement goes in the opposite direction. A number of isolationists in the Backgrounder Oort cloud population have apparently become aligned with the Solipsts, although the extent of this alignment is not entirely clear.
Related Articles
Appears in Topics
Development Notes
Text by Trolligi
Additional material by Steve Bowers
Initially published on 25 June 2003.
Updated Dec 2023 by Trolligi with additional material by Steve Bowers
Additional material by Steve Bowers
Initially published on 25 June 2003.
Updated Dec 2023 by Trolligi with additional material by Steve Bowers